BC 5200TX Series
Chapter 3 - Installation
BC5200TX Series Board Installation
Installation in a Cubix System
SCSI Device Installation
The board is equipped with an integrated fast/wide SCSI adapter. This adapter is enabled or disabled via the Chipset option of the BIOS Setup utility and via hardware with jumper JP6. The SCSI adapter is a bus master device which gains control of the PCI bus to transfer data between the CPU memory and the SCSI devices. The I/0 base address and interrupts are set by the PCI plug and play BIOS at boot time.A SCSI configuration utility is available on boot-up of the board. Shortly after the SCSI BIOS information displays, the configuration program can be accessed by pressing Control C. The configuration utility will allow you to scan the SCSI bus, change configuration options, and view a list of SCSI devices connected to the board. If the SCSI BIOS is inadvertently turned off in the SCSI configuration utility, turn it back on by holding <CTRL> A when the board is reset.
The Symbios SCSI adapter on the DP Series support:
Note: The SCSI adapter defaults to device 7.
SCSI Termination
On-board SCSI termination is controlled by dip switches 4 and 5 of switch S2. Normally, both switches are off, which terminates the high and low order bits of the SCSI bus.The following four diagrams show the switch settings for proper SCSI termination with SCSI devices connected to connectors J14 (50 pin) or J18 (68 pin).
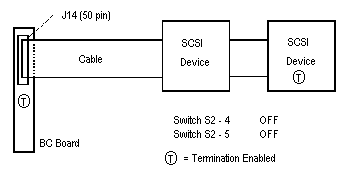
Figure 3-1, 8 Bit External OR Internal SCSI devices
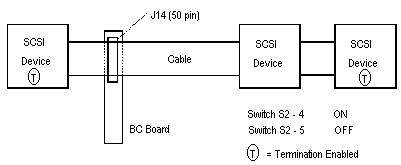
Figure 3-2, 8 Bit Internal AND External SCSI devices
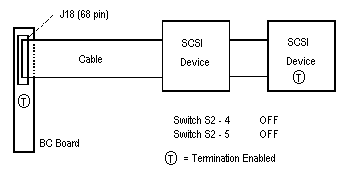
Figure 3-3, 16 Bit Internal OR External SCSI devices
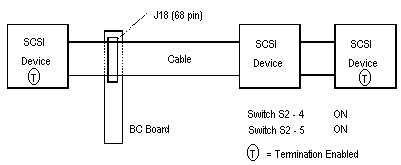
Figure 3-4, 16 Bit Internal AND External SCSI
devices
Note: Termination should also be configured as "enabled" if the SCSI interface is not used. The last device on the SCSI cable must also supply a termination load to the cable. SCSI devices not at the end of the cable must have their termination loads disconnected. Enabling and disabling a SCSI device's termination may involve a switch or shunt setting or the installation or removal of resistive SIP or DIP packages on their circuit board. Consult the installation manual for the SCSI device to determine its termination options.
PCI Extension Overview
The BC 5200TX boards support PCI bus extension via the connection of an optional PCI bus extender card. The extender card, which connects to the 80-pin connector at location J16 on the BC board, extends the PCI bus to an ERS/FT II PCI Master Interconnect Board (MIB). When installed in the ERS/FT II subsystem, the ISA connectors on the BC board and the PCI connectors on the PCI bus extender card simultaneously engage the ISA and PCI connectors on the MIB. The only subsystem that supports PCI extensions is the ERS/FT II.Two PCI extender cards are available, passive and active.
The passive extender card (figure 3-5) is used on PCI MIBs with one or two PCI expansion slots.
Figure 3-5, Passive PCI Extender Card
The active PCI extender card (figure 3-6) is equipped with a PCI-to-PCI bridge controller that extends the PCI bus to a maximum of four external controllers. The active PCI extender card is designed for use with MIBs having three to four PCI adapter slots for each BC Triton board installed. MIBs having fewer than three PCI adapter slots per BC installed will not support the active PCI extender card. The only MIB supporting the active card is the 2x5 PCI + 2x2 ISA.
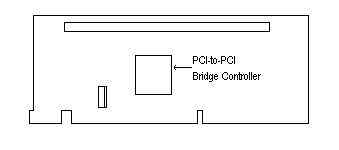
Figure 3-6, Active PCI Extender Card
Note: The ERS/FT II PCI MIB's have dedicated bus master positions that accept BC
boards equipped with the PCI bus extender card. Care should be taken to see that edge
connectors on both the BC board and the extension card are properly aligned before
inserting them into the MIB slots.
Optional Peripheral Adapter Installation
Optional Cubix peripheral adapter boards are available for VKM (Video/Keyboard/Mouse), LPT1, and COM 2. To install the adapters, follow the steps listed below.WARNING!
MAKE SURE THE SYSTEM IS POWERED OFF AND
UNPLUGGED BEFORE BEGINNING THIS PROCEDURE.
Ethernet 10/100 Base-T Installation
The board is equipped with an integral DEC 21140 PCI fast Ethernet controller with a RJ-45 10/100 BASE-T connector on the mounting bracket at the rear of the board. This adapter is enabled or disabled via the "Chipset" option of the BIOS Setup utility and via hardware with jumper JP6. The I/O addresses and interrupts are set by the PCI plug and play BIOS at boot time. Software drivers are provided for this controller to support PC local area networks.Near the RJ-45 connector and visible in the mounting bracket are two sets of light emitting diodes (LED). On the lower set, the green LED will light when the interface has a valid connection to an Ethernet hub. The amber LED will light when the interface is set to 100 Mbit/s. On the upper set, the green LED indicates network activity, and the amber LED indicates a data collision on the network. These LEDs can be useful indicators of network activity.
Line Busy Installation
The Line Busy RJ-11 jack is designed to be connected to the phone line that attaches to a modem. Its purpose is the make the telephone line appear busy when the processor or modem is not ready to answer an incoming telephone call.The Line Busy circuit is inserted in parallel with the telephone line from the PBX to the modem. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has registered this circuit for use on PBX systems only and not for direct connection to the Public Telephone Network.
The Line Busy circuit is designed to be used on rotary PBX systems to keep incoming calls from ringing on lines that will not answer. The circuit uses Data Terminal Ready (DTR) from the Cubix processor's communication port to determine whether the processor is ready for a call. If DTR is false, the circuit creates an off-hook condition on the telephone line to force the rotary PBX to bypass this extension for an incoming call. When DTR is true, the Line Busy Circuit will terminate the off-hook condition, and the processor will respond to an incoming call. The Line Busy circuit on the SP is controlled by the COM1 DTR signal. The COM2 port has no effect on Line Busy. Cubix processors assert DTR false on the reset operation. It is the responsibility of the communications application running in the processor to assert the DTR signal true.
WARNING!
The line busy circuit integrated onto the BC (J12) has been registered with the Federal Communications Commission for use on PBX's in the United States only. Use of this function outside the United States may violate local regulations and is not recommended by Cubix Corporation. The line busy circuit complies with Part 68, FCC Rules.FCC REGISTRATION NUMBER
2HEUSA-73508-KX-N
RINGER EQUIVALENCE O.O.B.
Line Busy Installation
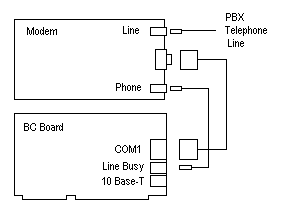
Figure 3-7, Line Busy Hook-up with Modem Phone Jack
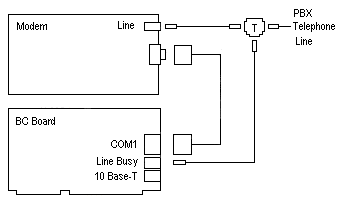
Figure 3-8, Line Busy Hook-up with Modem Phone Jack
This document, and all Web contents, Copyright © 2000 by Cubix Corp., Carson City, NV, USA.